By Ling Huawei, managing editor of Caixin Media and Caixin Weekly. Originally published in Caixin,
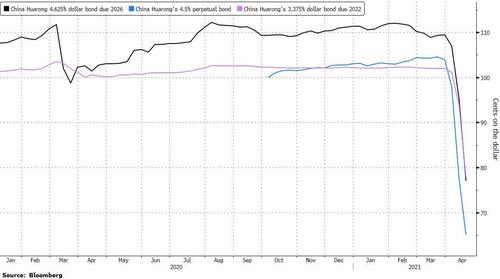
After China Huarong Asset Management Co. Ltd. on March 31 decided to suspend its share trading the next day, the market became awash in rumors that the company, one of the country’s four largest bad-asset managers, would be forced into restructuring or might even go bankrupt (as we discussed in "This Is A Fatal Event": China's Bond Market Hammered After Huarong Bankruptcy Rumors).
The rumors spooked many institutional investors, sending the company’s bonds tumbling. Huarong, a product of China’s reform of state-owned banks at the end of last century, has once again found itself at the center of a critical moment in its history.
But can Huarong go bankrupt?
Huarong is not a bank. Most of its investors are the institutional sort, not individuals. If it were to go bankrupt, the spillover risks ought to be much easier to handle. Also, although Huarong has total assets upward of 1.7 trillion yuan ($259 billion), the central bank does not regard it as a systemically important financial institution. Therefore, it seems that Huarong’s problems ought to be dealt with in the same “market-oriented” way as average financial institutions. Under China’s Company Law in the case, shareholders would need to fill the holes on the books with net assets. After that, the company could issue new shares or introduce strategic investors to supplement the company’s capital. If the company was still insolvent after all that, it might end up facing debt restructuring or bankruptcy.
However, Huarong is not an ordinary company. Rather it is a central government-administrated state-owned financial enterprise. At the end of last century, the company was set up to dispose of the nonperforming assets of state-owned Industrial and Commercial Bank of China Ltd. Since 2006, it gradually expanded into a financial holding company. Huarong’s biggest shareholder is the Ministry of Finance, which holds a 61.25% stake. Huarong has grown its business mainly by obtaining financing with a state guarantee. In July 2014, the company started issuing bonds overseas, the outstanding value of which is more than $23 billion.
Huarong, which went public in Hong Kong in October 2015, provides financing to multiple industries, with a large portion of its investment flowing into the property market or other areas where bank lending is kept under tight restrictions. Excluding its subsidiary, Huarong Xiangjiang Bank Corp. Ltd., Huarong has around 1 trillion yuan in assets, connecting financial institutions including banks, trust firms and insurance firms and nonfinancial industries. That gives Huarong certain characteristics of a systemically important financial institution that probably shouldn’t be allowed to go bankrupt.
Regardless of whether it ends up going bankrupt, Huarong will need to put under strict financial constraints. Lai Xiaomin, a former chairman of Huarong who came under investigation in April 2018, was sentenced to death this January in the country’s biggest financial corruption case since the founding of the People’s Republic of China in 1949. Some believe that Lai’s misconduct as chairman left Huarong with a huge financial black hole. The complexity of Lai’s case made it difficult to unwind some of Huarong’s more problematic projects, so it’s unrealistic to expect Huarong to fill that hole all on its own.
As of mid-2020, Huarong had 160 billion yuan in net assets, and more than 30 billion yuan in loan-loss provisions. Huarong needs to be thoroughly recapitalized and have the value of its nonperforming assets correctly recalculated. It needs to “take a big bath.” Unless it does so, the company’s moral hazard will continue to grow. The financial black hole won’t disappear on its own, so Huarong needs to take responsibility and shoulder the losses.
There’s no making without breaking. “Breaking” does not mean a hasty debt restructuring or even bankruptcy, but a practical restructuring plan created after completely clarifying its assets and liabilities. “Making” means Huarong needs to have the professional capabilities to dispose of nonperforming assets, to become a professional institution that can effectively dispose of such assets at both home and abroad.
To achieve this goal, Hong Kong-listed Huarong will need the support and understanding of shareholders and other investors so that it can be privatized and delisted if necessary. Also, it needs to clear up its financials and recalculate its loss provisions. It will also need to reduce the costs of restructuring as much as possible and once again become a professional institution by reshaping its corporate culture and improving its internal governance.
Update
Confirming the above, this morning Bloomberg reported that Huarong has prepared funds for full repayment of a S$600 million offshore bond due April 27, according to a person with direct knowledge of the company’s plan.
Huarong plans to make the payment on the due date, while a Huarong spokesperson declined to comment but said the company has “adequate liquidity” and has made full repayment on bonds that have matured
Huarong International, the main offshore arm of China Huarong, “will continue its stable and compliant operations based on new business development plan,” the spokesperson said.








0 comments:
Post a Comment